Formulas & Tools
Two parameters completely specify an etalon: the free spectral range (FSR) and the finesse (ℑ). The FSR is the spacing (usually given in frequency) between transmission peaks.
The finesse is the ratio of the free spectral range to the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the transmission peak and is directly related to the reflectivity of the surface R.
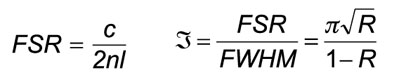
c is the speed of light, n is the index of refraction of the etalon, and L is the thickness of the etalon.
At high finesse values (where R is very close to 100% or 1), R≈1-π/ℑ
| Finesse | Reflectivity |
| 2 | 24% |
| 4 | 47% |
| 6 | 60 % |
| 8 | 68 % |
| Finesse |
Reflectivity |
| 10 | 73 % |
| 15 | 81 % |
| 20 | 85 % |
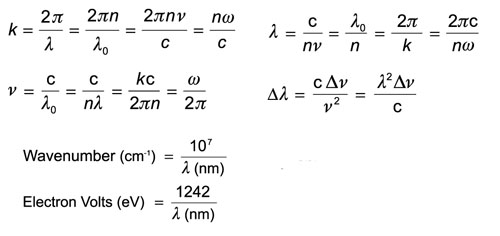
An easy number to remember is a 1-pm linewidth is approximately 125 MHz ar 1550 nm.
where
k = wave vector; v = frequency; w = 2πv = angular frequency; λ = wavelength; λ0 = wavelength in vacuum; n = refractive index
| Wavelength (in vacuum), nm | Frequency, THz | Electron Volts, eV | Wavenumber, cm-1 |
| 1561.42 | 192.00 | 0.80 | 6404.43 |
| 1550 | 193.41 | 0.80 | 6451.61 |
| 1320 | 227.12 | 0.94 | 7575.76 |
| 1064 | 281.76 | 1.17 | 9398.50 |
| 980 | 350.91 | 1.27 | 10204.08 |
| 780 | 384.35 | 1.59 | 12820.51 |
| 632.8 | 473.76 | 1.96 | 15802.78 |
| 350 | 856.55 | 3.55 | 28571.43 |
| Factor | Name | Symbol |
| 1021 | zetta | Z |
| 1018 | exa | E |
| 1015 | peta | P |
| 1012 | tera | T |
| 109 | giga | G |
| 106 | mega | M |
| 103 | kilo | k |
| 102 | hecto | h |
| Factor | Name | Symbol |
| 10-2 | centi | c |
| 10-3 | mili | m |
| 10-6 | micro | µ |
| 10-9 | nano | n |
| 10-12 | pico | p |
| 10-15 | femto | f |
| 10-18 | atto | a |
| 10-21 | zepto | z |
| 10-24 | yocto | y |
| Material | Refractive index, n | ∆FSR*, MHz | Thermal Expansion Coefficient α, ppm/°C | Thermo-Optic Coefficient β or ∂n/∂T, ppm/°C ° |
| Air | 1.0000 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Fused Silica | 1.444 | 13.1 | 0.55 | 6.57 |
| Silicon | 3.477 | 198.1 | 3.24 | 160 |
| LASFN9 | 1.813 | 9.4 | 7.4 | 1.3 |
* Change in FSR due to dispersive effects as measured from 1510 to 1570 nm for a 50 Ghz etalon
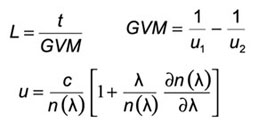
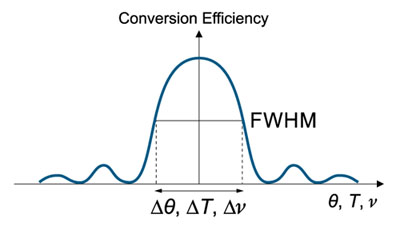
Nonlinear Crystal acceptances – Angular Δθ, Temperature ΔT, Spectral Δv – corresponding bandwidths at Full Width of Half Maximum (FWHM) of conversion efficiency.
Polar coordinate system for description of refractive properties of uniaxial crystal.
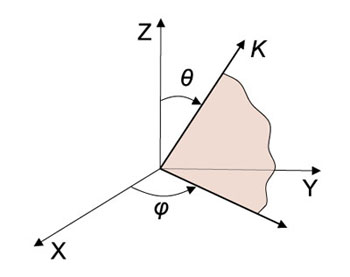
Whereas K – light propagation vector at phase matching conditions, Z – optical axis of crystal, θ – phase matching angle (or cut angle), φ – azimuthal angle.
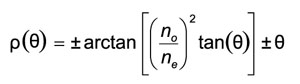
Upper signs refer to negative crystal (no>ne) and the lower signs refer to positive one (ne>no).
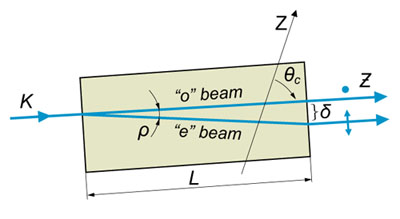
Beam displacement because of walk–off:
Δ = L tan (ρ)
Whereas L – crystal length, ρ – walk-off angle.
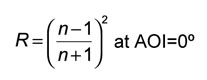
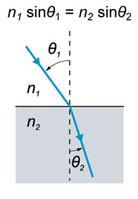
Where n-refractive index, AOI - angle of incidence.
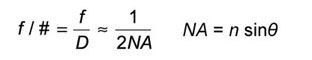
The angle where only s-polarized light is reflected
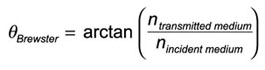
A Gaussian beam spreads as follows,
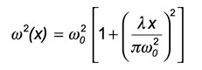
where w(x) is the 1/e2 radius, λ is the wavelength, and x is the distance from the beam waist w0 where x=0.
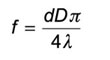
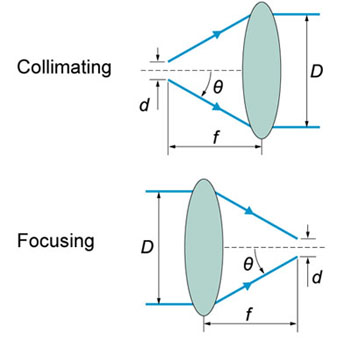
Where f is the lens focal length, d is the beam diameter at the focus, D is the 1/e2 diameter of the collimated beam.
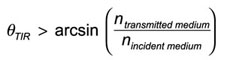
Where ntransmitted medium<nincident medium is required for total internal reflection.
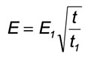
Where E [J/cm2] is the damage threshold, t is pulse duration, E1 and t1 are the reference damage threshold and pulse duration.
Negative crystals (no>ne)
Type 1 ko1+ko2=ke3(θ) or “ooe interaction”
Type 2 ke1(θ)+ko2=ke3(θ) or “eoe interaction”
Type 2 ko1+ke2(θ)=ke3(θ) or “oee interaction”
Positive crystals (ne>no)
Type 1 ke1(θ)+ke2(θ)=ko3 or “eeo interaction”
Type 2 ko1+ke2(θ)=ko3 or “oeo interaction”
Type 2 ke1(θ)+ko2=ko3 or “eoo interaction”
Whereas k-wave propagation vector (k=2πn/λ); θ – phase matching angle in the crystal; o – ordinary polarization, e – extraordinary polarization; 1, 2, 3 indices – corresponds to wave vectors with longest (1), mid (2) and shortest (3) wavelengths.
NCPM – when crystal phase matching angle equals 90º (θ = 90º). NCPM is achieved at special temperatures and/or wavelengths.
Planck’s constant h = 6.6260755×10-34 J⋅s = 4.5×10-15 eV⋅s = 6.626×10-27erg⋅s
Dirac’s constant ħ = h/2π = 1.054×10-34 J⋅s = 1.054×10-27erg⋅s
Boltzmann’s constant kB = 1.380×10-16 erg/K = 8.62×10-5 eV/K = 1.380×10-23 J/K
kT = 25.9 meV at room temperature
= 0.36 meV at liquid-helium temperature (4.2 K)
= 6.7 meV at liquid-nitrogen temperature (4.2 K)
Velocity of light in vacuum c = 2.99792458×108 m/s
Electron charge e = 1.602×10-19 coulombs
Avogadro number Na = 6.0221367×1023 particles/mol
Permeability of vacuum μ0 = 4×10-7 T2⋅m3/J
= 12.566370614×10-7 T2⋅m3/J
Permittivity of vacuum ε0 = 1 / (μ0⋅c2)
= 8.854187817×10-12 C2/J⋅m
Electron rest mass me = 9.1093897×10-31 kg
Proton rest mass mp = 1.6726231×10-27 kg
Neutron rest mass mn = 1.6749286×10-27 k
- Address: Dvarcioniu st. 2B LT-10233 Vilnius, Lithuania
- Phone: (+370) 5 272 99 00
- Fax: (+370) 5 272 92 99
- E-mail: info@eksmaoptics.com